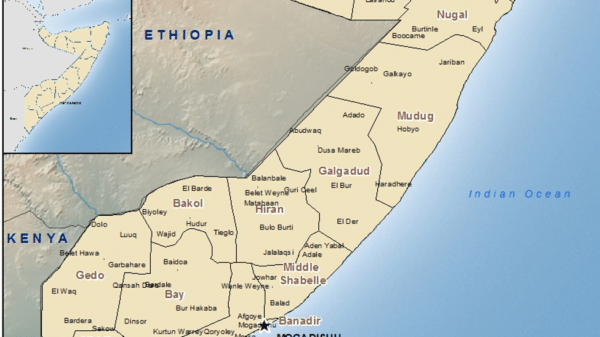
Somalia, a country located on the eastern coast of Africa, holds a unique position due to its historical interactions with various cultural and ethnic groups. This article delves into different topics surrounding the identity, religion, international relations, and security concerns of Somalia. We explore the intricate web of influences that have shaped this nation and its people. Topics Covered:
Somali Identity
The Somali people primarily identify themselves as Cushite African. Somalia is indeed located on the African continent, with its population primarily consisting of ethnic Somalis. Throughout history, Somalia has been influenced by the trade routes of the Arabian Peninsula, resulting in certain cultural and linguistic similarities with Arab countries. However, it is important to note that Somalis predominantly consider themselves Africans due to their geographical location and historical ties with the African continent.
1. Are Somalis African or Arab?
The Somali people primarily identify as African, belonging to the Cushitic ethnic group. While they share genetic and linguistic ties with Arab populations, it is important to note that their cultural practices and heritage are mainly influenced by their African roots.
2. Are Somalis Indian?
Although Somalia holds historical connections to India through trade activities, the overwhelming majority of Somalis are not of Indian descent. However, it’s worth mentioning that the Indian Ocean trade route has had significant cultural exchanges between India and Somalia.
3. Are Somalis Habesha?
The term “Habesha” typically refers to people inhabiting the Horn of Africa region, including Ethiopia, Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalis in the past. However, the majority of Somalis identify themselves distinctively as Somali within the Cushite family and have a unique cultural heritage separate from the Habesha Sematic groups in Ethiopia, consisting of the Tigre, the Agew, The Beta Israel and the Amhara
Somalia Faith
4. Is Somalia predominantly Muslim?
Yes, Somalia is predominantly Muslim, with nearly 99% of the population adhering to Islam. Islamic traditions and values heavily influence Somali society, shaping various aspects of life, including politics, governance, and social norms. Islam is the predominant religion in Somalia. The Muslim faith spread to the region during the 7th century through Arab traders and has since remained deeply embedded in Somali culture. Islamic principles and practices have greatly influenced Somali society, including its legal systems, social norms, and everyday life.
Somalia and Ethiopia
Somalia and Ethiopia, both located in the Horn of Africa, share a complex history with each other. While there have been periods of conflict and tension between the two countries, they have also experienced periods of cooperation and alliance. Historically, Somalia and Ethiopia have overlapping ethnic communities, such as the Somali and Oromo people, which has at times fueled tensions as well as issues related to border disputes. The relationship between Somalia and Ethiopia continues to evolve and vary depending on political circumstances.
5. Are Somalia and Ethiopia allies?
Somalia and Ethiopia have experienced strained relations throughout history due to border disputes, ethnic clashes, and ideological differences. They have been at war in the past, but currently, both countries maintain diplomatic relations and occasionally collaborate on certain issues.
6. Are Somalia and Ethiopia the same?
Despite some shared historical and cultural ties, Somalia and Ethiopia are distinct countries with unique identities, political systems, and languages. While there may be some overlaps in certain regions, both nations have their own distinct histories, languages, and traditions.
Somalia and Somaliland
7. Are Somalia and Somaliland the same?
Somaliland is a self-declared independent region within Somalia, but it is not internationally recognized as a separate country. While Somaliland and Somalia share ethnic and cultural ties, they have separate administrations and political aspirations.
Somali Pirates
8. Are Somali pirates still a threat?
Somali piracy, which reached its peak in the late 2000s, has significantly reduced due to international efforts and strengthened maritime security in the region. However, sporadic incidents still occur, highlighting the need for continued vigilance to address piracy concerns. Somali pirates gained international attention in the early 2000s due to their piracy activities in the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean. However, in recent years, international efforts, including naval patrols and improved shipping security, have significantly curtailed the threat of Somali piracy. While sporadic incidents may still occur, the presence and impact of Somali pirates have significantly diminished compared to previous years.
Somalia and China
9. Are Somalia and China allies?
Somalia and China have maintained diplomatic relations since 1960, with China providing aid and investments in infrastructure development, education, and healthcare. Though not formal allies, the relationship between the two nations has deepened over the years. Somalia and China have developed closer ties in recent years. China has increasingly invested in infrastructure projects in Somalia, such as port developments and roads. Additionally, China has provided humanitarian and developmental aid to Somalia, contributing to its reconstruction efforts. However, it is crucial to note that Somalia maintains diplomatic relations with multiple countries and is not exclusively aligned with China.
In Summary: Somalia’s identity is shaped by its African heritage, Islamic religion, and interactions with different cultures and nations. Although historical ties connect Somalia to Arab, Indian, and Ethiopian influences, the Somali people have their own distinct identity. Moreover, Somalia’s political landscape is marked by the complex relationships it shares with Ethiopia, Somaliland, and the international community. While the Somali piracy issue has decreased, it is crucial to remain vigilant. Overall, Somalia stands as a vibrant nation rooted in its African identity while being open to diverse influences from around the world.
Somalia’s identity primarily reflects its African roots, although the influence of Arab culture is also evident. The Somali people predominantly practice Islam, which plays a significant role in their daily lives and societal norms. Historically, the relationship between Somalia and Ethiopia has been multifaceted, with periods of collaboration and conflicts. While Somali pirates were a significant concern in the past, international efforts have diminished their threat. Lastly, Somalia has developed closer ties with China through infrastructure projects and aid. However, Somalia maintains diplomatic relations with multiple nations and is not exclusively aligned with China.